Australian EVS can work with you to understand what charging solution works best for you.
You need to consider whether you want to be connected to the mains or use solar for a true zero emission option, then the type of charging station, along with the type of cables and plugs you will need.
Whether you are looking to install a single charge point in your home, several at your place of work or a network in an apartment block, we can assist along with our network of suppliers to bring you the best package.
EV CHARGING STATIONS
Types of Chargers
Existing power point (10-15 Amp, single phase) used in combination with a specialised cable, which is typically supplied with the vehicle.
Typically used in standalone domestic homes.
This method will add between 10 and 20km of range per hour plugged in.
It will top up daily use, but will not fully recharge a typical pure electric vehicle overnight.
A dedicated AC EV charger at up to 7kW (32 Amp, single phase).
Typically installed in homes, apartment complexes, workplaces, shopping centres, hotels, etc. – anywhere the vehicle will be parked for a while.
This method will add up to 40km of range per hour plugged in.
It will top up average daily vehicle use in an hour or deliver a full recharge overnight.
A dedicated DC EV charger at power levels from 25kW to 350kW (40 – 500 Amp, three phase).
Typically used in commercial premises and road-side locations to provide for faster recharging than Level 1 and 2 can achieve.
At the lower end, this method will add up to 150km of range per hour plugged in.
At the upper end, this method can fully recharge some electric vehicles in 10 to 15 minutes.
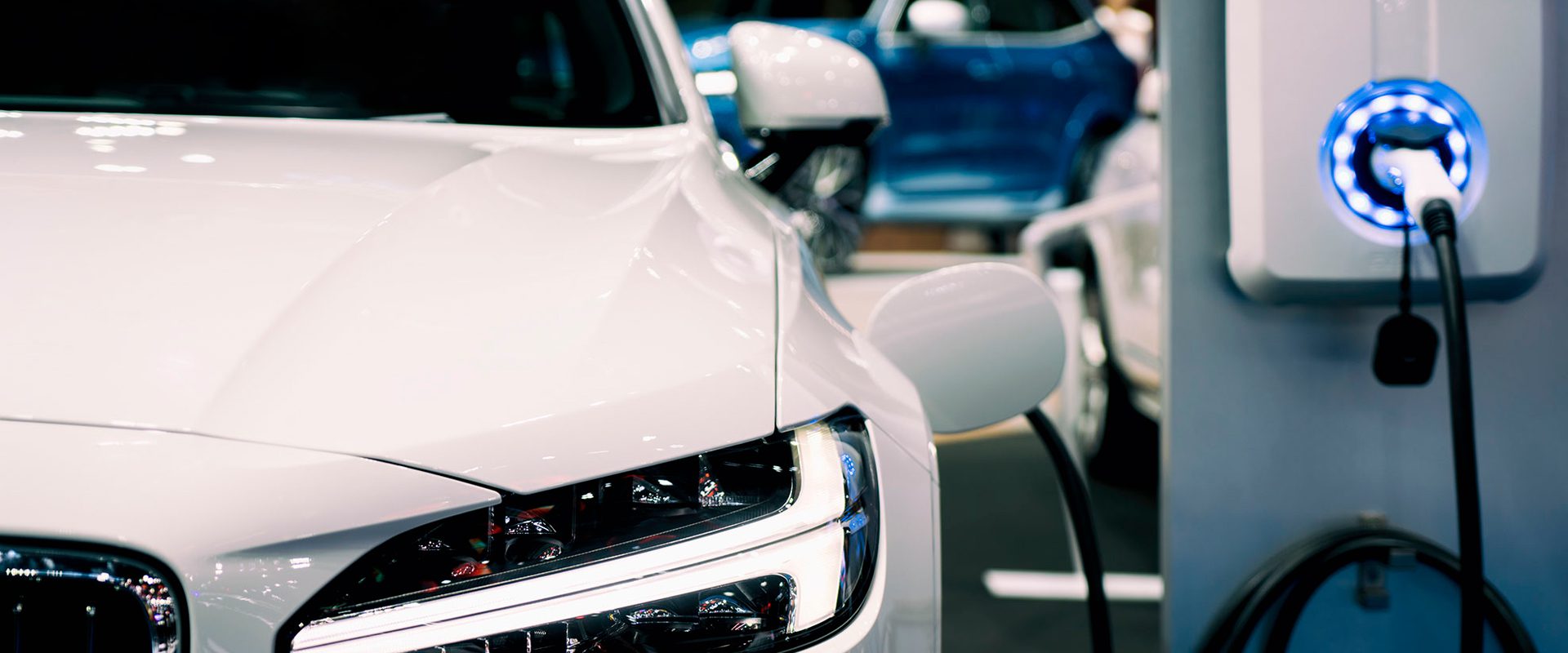

EV CHARGING AT HOME
Residential charging stations generally consist of a charging box with the control unit mounted to the wall or a pole, if desired. Charging stations come with a fixed cable and a connector suited to your vehicle. We also stock a range of adapters that allow you to charge different electric vehicles if you have several vehicles in your household.
FURTHER EV CHARGING CONSIDERATIONS
We can provide all-inclusive prices for standard residential installations which apply to around 80% of residential customers.
There are, however, factors that may increase the cost of installation. These include, but are not limited to:
- How far the parking lot is from the distribution board
- Whether wall openings or excavation work is required
- If an additional stand is required to mount the charging station as opposed to wall mounting
- Whether there is already a cable that can be utilised, instead of having to lay a new cable
Equally important are the electrical security elements. Every charging station for electric cars must have its circuit protected by a circuit breaker and a residual current device. The residual current circuit breaker is already integrated for some charging stations, considerably reducing installation costs. These points can be discussed in more detail – simply get in touch.
HOW TO CHOOSE WHICH EV CHARGER YOU NEED
Whether you already own a new EV, are looking to convert your vehicle to electric, or looking to install chargers in Commercial premises to generate revenue, we can assist.
We have a range of suppliers who can inspect your site and available power supply in order to provide you with a comprehensive quote.
THE ENERGY COSTS OF CHARGING AN EV
In Australia, depending on state and tariff, the average electricity cost is between 27c and 43c per kWh. A distinction is often made between the on-peak and off-peak tariff. If you charge your electric vehicle during off peak times, you benefit from a cheaper electricity price per kWh. However, not all electricity providers distinguish between on-peak and off-peak rates. Larger companies often negotiate a special electricity tariff with their energy supplier.
In order to calculate the amount of energy used by your charging station over a 12-month period, simply multiply power consumption in watts or kilowatts by the number of operating hours over the year.
If you charge your electric vehicle for an average of three quarters of an hour at night on your 22 kW charging station, this results in an annual energy consumption of 6022.5 kWh = 0.75 h x 22 kW x 365 days.
After you have determined the annual energy consumption, simply multiply the amount of energy with the electricity tariff of your energy provider. At a rate of 15 cents per kWh, the annual electricity costs amount to around $903.38 (or 6022.5 kWh x $0.15).
For the sake of simplicity, we have not factored in the power loss in the above example. This results from the fact that each charger and each accumulator has an individual efficiency. The effective energy costs can therefore be up to 10% higher, depending on the respective efficiency of the charging infrastructure used and the power electronics installed in the electric vehicle.

AC VS DC CHARGING FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES
ALTERNATING CURRENT

7.4 kw
Type 1 ♂
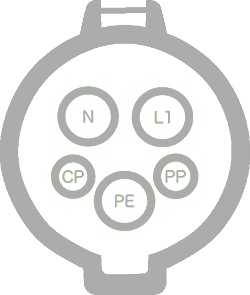
7.4 kw
Type 1 ♀

44 kw
Type 2 ♂

44 kw
Type 2 ♀
DIRECT CURRENT
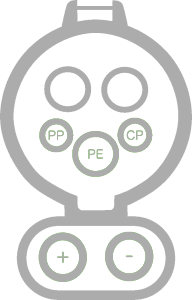
350 kw
Type 1 ♀ CSS

350 kw
Type 2 ♀ CSS
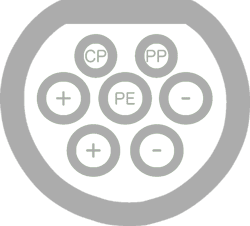
120 kw
Tesla Supercharger ♀

400 kw
CHAdeMO ♀
THINGS TO CONSIDER BEFORE PURCHASING AN ELECTRIC CHARGER
Before committing to a charging solution, it is best to consider the following four points: mains connection, charging station, charging cable and electric vehicle – which must be observed if you are aiming for the shortest possible charging times. If just one of these four factors is rated at a lower capacity than the rest, the charging time of your electric vehicle will increase according to the weakest link in the charging chain.
